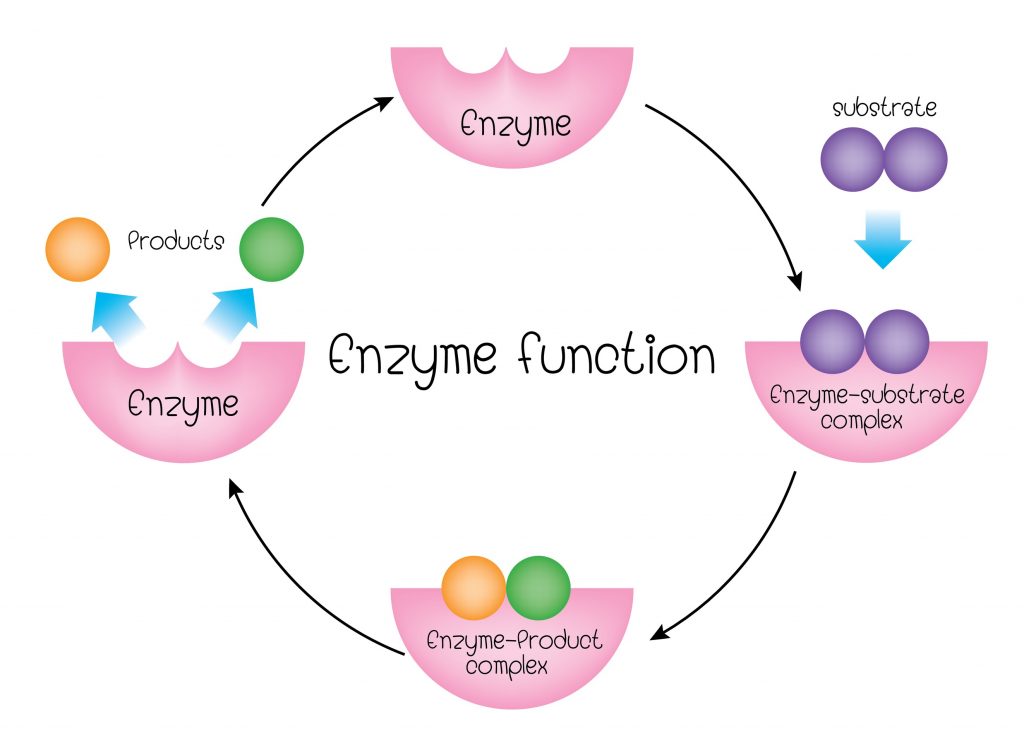
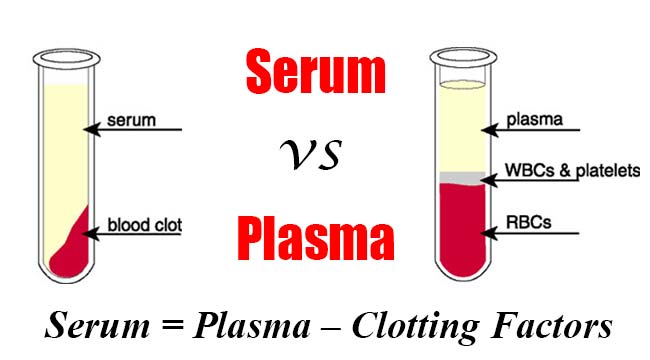
Biochemistry of Urine or Urine analysis or Urinalysis or Urine-R&M(routine and microscopy)
Urine is an excretory product of the body and presence of certain substances in urine reflects the metabolic state of the body. Composition 95% of volume of normal urine is due to water. Others:- Organic components – urea, urobilinogen, uric acid, amino acids, creatinine, metabolities of hormones. Inorganic components – Cations:- Na+, K+, Ca2+, NH4+ …