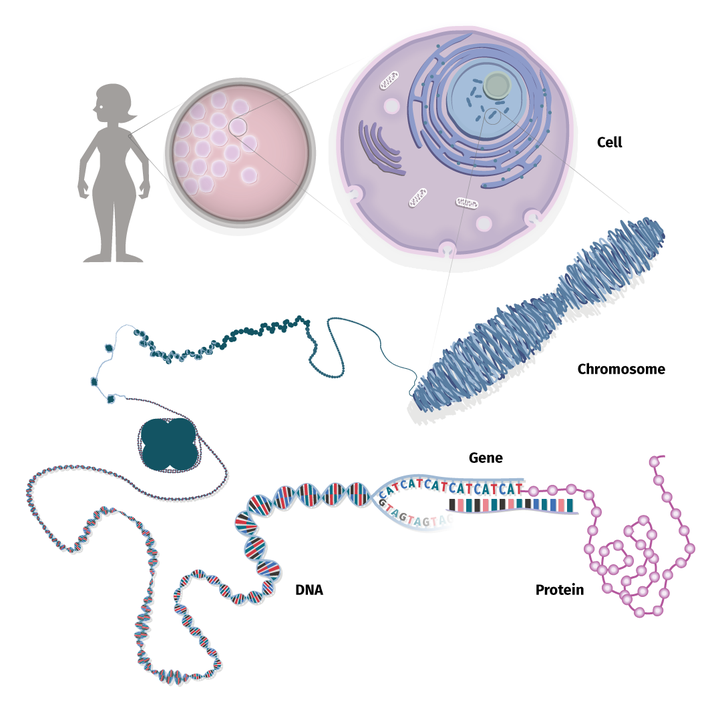
MENDELIAN THEORY OF INHERITANCE
INTRODUCTION Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Modern Genetics. He studied approximately 29000 pea plants to demonstrate inheritance of traits following certain laws. For seven years, Mendel bred pea plants and recorded inheritance patterns in the offspring. He studied seven characteristics in the garden pea. WHY A PEA PLANT Flower structure of pea plant ensured …