It is the area of chemistry that is generally concerned with analysis of body fluids for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is an applied form of biochemistry.
Various biological fluids subjected to chemical tests and assays include :-
- Blood
- Plasma
- Serum
- Urine
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Ascetic fluid
- Pleural fluid
- Stool
- Calculi and Tissues
- Gastric juices
- Saliva
- Amniotic fluid.
Fluids / Specimens helps in:-
- Diagnosis
- Progression of disease
- Response/effectiveness of treatment/medication
- Screening
- Prevent complications
- Predict survivability
Choice of specimen depend on:-
- Analyte to be measured
- Ease of collection.
Specimens tested in clinical analysis:-
- Serum
Most common specimen tested. It is obtained by centrifugation of coagulated blood. Serum contains no blood cells or clotting factors but has electrolytes, hormones, antigens, antibodies, and other substances such as drugs, microbes, and proteins (not used in coagulation).
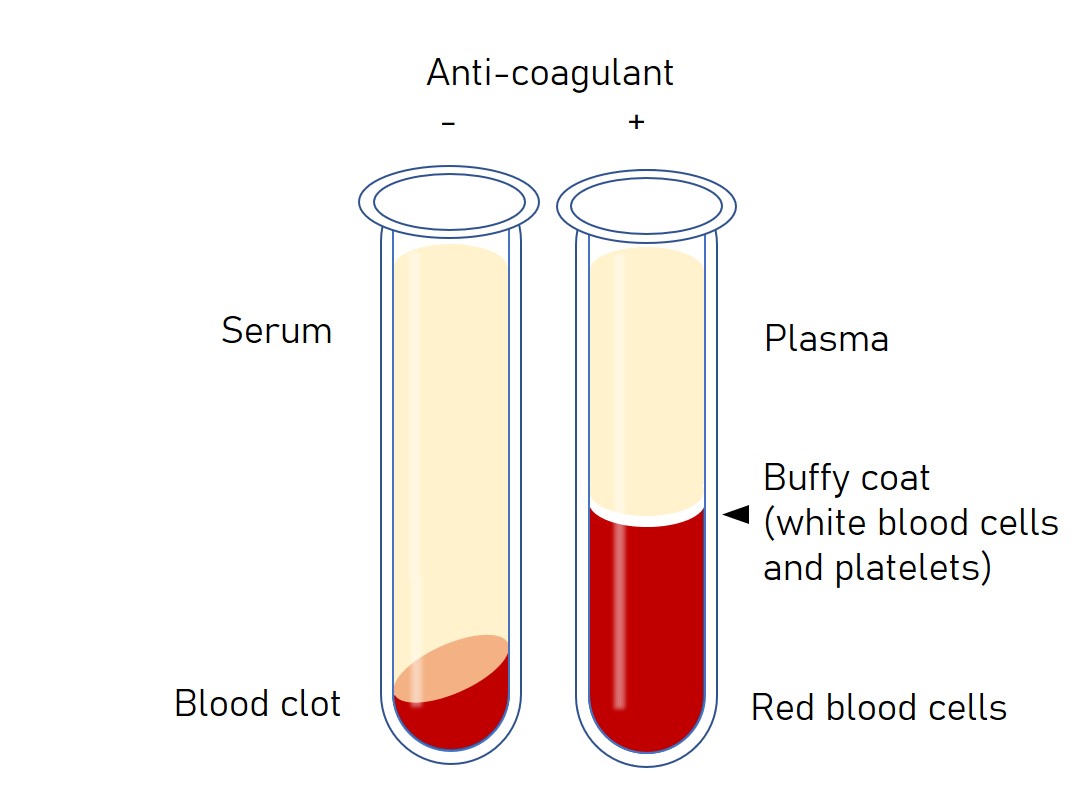
- Plasma
It is obtained by centrifugation of uncoagulated blood. It contains blood cells, clotting factors, glucose, electrolytes (Na, Mg, Ca, Cl,K), hormones, and proteins (albumin, fibrinogen, globulins),
- Urine
Urine is one type of specimen that can be easily collected from a patient. Urinalysis testing can give the doctor valuable information about many body systems especially kidney function.

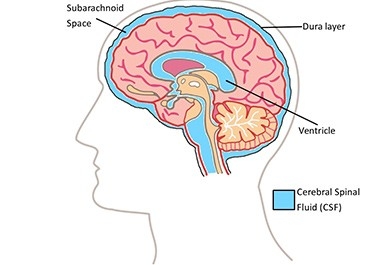
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
It is a clear fluid present in brain and spine. Which is largely similar to blood plasma though it differs by containing nearly no protein.